
Common Name: Giant Banjo Frog, Giant Pobblebonk, Giant Bull Frog
Scientific Name: Limnodynastes interioris
Family: Myobatrachidae – Australian Ground Frog family
Location: Australia – New South Wales
Size: 2.8 – 3.5 inches (7 – 9 cm)
The Giant Banjo Frog spends its days burrowed under ground and comes up during the night to hunt. During the drier months, they spend the whole time underground. Their strong hind legs help them with the burrowing.
The male Giant Banjo Frog calls from August to April, peaking during the Australian spring. They call while floating on vegetation in dams, swamps, and slow moving creaks or just call from their burrows. Once the female frog arrives, the male Pobblebonk grasps the female frog from behind. Then, the female frog lays her eggs and the male frog fertilizes them. The female Banjo Frog can lay up to 4000 eggs. The eggs hatch into tadpoles a few days later. The tadpoles take around 2 and a half months to complete their metamorphosis into frogs. Neither parent provides any parental care to their offspring.
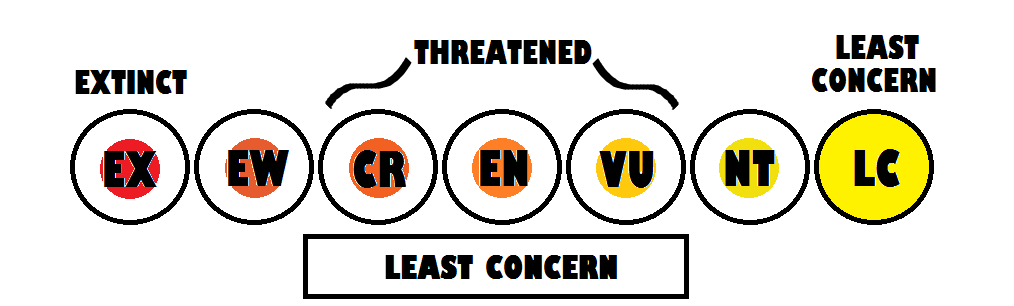
The International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List assesses the Giant Banjo Frog as Least Concern for Extinction. They have a large range and a presumed large population as well. A potential threat to the species is farming in the region.

